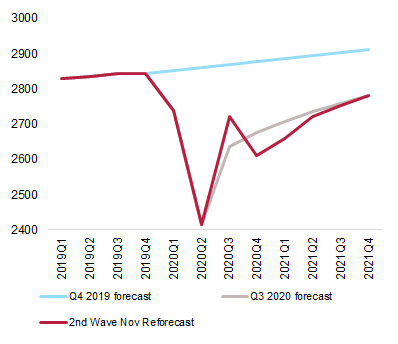
Thirdly, our worries regarding the corporate bonds segments have increased, notably for the high-yield segment, as lending to insolvent businesses is not part of central banks’ classic job description. Corporate bonds have attracted a lot of fresh capital since March in the wake of central banks’ policy announcements in favor of investment grade bonds (and fallen angels in the U.S., with the ECB possibly jumping on the bandwagon as soon as December). However, especially in the EMU, it would be a mistake to assume that the central bank can backstop any kind of corporate bonds regardless of their creditworthiness. National Treasuries will have to do that job, hopefully but not necessarily in a timely manner. Spreads at the lower end of the credit spectrum will therefore widen. In EMs, even if the long-term growth outlook is more attractive than in DMs, an operating earnings long-term growth forecast of +19% provides little cushion against adverse outcomes. Owing to past currency depreciation, local currency bonds offer some value, but at the cost of elevated volatility. Despite some recent correction, hard currency bonds still look overpriced.
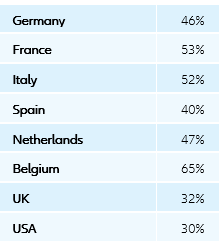
Country focus: The costs of 'lockdown light' in Germany, France, Italy, Spain and the UK
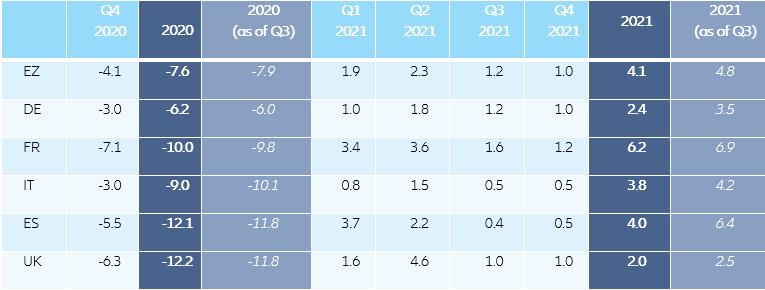
For Germany Chinese demand as a “pillar of stability” will prove ever more important in the coming months as key trading partners are tightening Covid-19 restrictions to battle the second virus wave. In Germany, GDP jumped by +8.2% q/q in Q3, with the annual rate recovering from -11.3% to -4.3%. Following the announcement of a four-week lockdown in November to save Christmas, we now expect a contraction of -3% q/q for Q4 2020 (-7% m/m in November - around 50% of the April shock), followed by a relatively muted rebound of +1% in Q1 2021 as social distancing restrictions are likely to remain elevated until Easter 2021. The renewed lockdown will delay but not derail the German economic recovery also thanks to the announcement of additional fiscal support to the tune of EUR10bn and the expected extension of flagship fiscal policies, including public credit schemes until at least mid-2021. A tailwind from China is one additional factor that has contributed to Germany emerging faster and in a better position from the Covid-19 shock relative to its European peers. After all, about half of EU-27 exports to China are from Germany. As German export prospects are bound to take a hit with a Eurozone Q4 growth double-dip all but certain, relatively more resilient Chinese export demand provides a ray of light amid the doom and gloom. In fact, out of Germany’s top 10 trading partners, China stands out as the only country that we expect to avoid a pronounced tightening in Covid-19 restrictions. All in all, German GDP looks set to contract by -6.2% in 2020 vs. -6% expected previously, followed by a more muted recovery in 2021 of +2.4% vs. +3.5% previously. As a consequence, we expect the German economy to recover to pre-crisis GDP levels only in late 2022.
In France, the stronger-than-expected economic recovery in Q3 (+18.2% q/q) ought to be short-lived as the economy will slide into a strong double-dip recession in Q4. French GDP rebounded by +18.2% in Q3, driven by strong base effects post lockdown but also by robust consumer spending during the summer. However, with increasing infection rates, both consumer spending and confidence deteriorated in September. The failure of partial containment measures to curb the explosive spread of the virus resulted in a return to a national lockdown as of November. France is implementing a lighter version of the March-April lockdown, with one third of the economy being put on pause for at least four weeks. We expect a less severe loss of economic activity (-16% compared to pre-crisis levels) this time around compared to the previous lockdown (-30%). However, in view of the saturated hospital capacity in most cities, we expect the national lockdown to be extended in December (for at least two more weeks) and be lifted only partially (with curfews in place) during the end-year holiday season. Overall, we expect GDP to plummet by -7.1% q/q in Q4 2020, bringing the annual contraction in 2020 to -10% (from -9.8% expected previously). The second wave of the pandemic will take its toll on the economy, causing severe output losses in already weakened sectors (tourism, hospitability, recreation, and transport and retail trade). Significant fiscal relief measures have been reinstated. In November, the French government announced an additional EUR20bn (1% of GDP) support package by reloading the partial unemployment scheme and the Solidarity Fund. This constitutes the 4th amendment to the 2020 finance law, and will bring the fiscal deficit to -11.3% of GDP in 2020 (up from -10.2%). In 2021, we expect stringent sanitary measures to remain in place in January and February, before being progressively relaxed as of March. Thus, we project a moderate rebound of activity (+3.4% q/q) in Q1 2021. Domestic demand is expected to bounce back with the progressive re-opening of the economy in Q2 2021 (+3.6% q/q). Under the impulse of the EUR100bn stimulus package and positive confidence effects following the start of the vaccination campaign we expect a robust recovery in H2 2021. Yet, we have revised our growth forecast down for 2021 to +6.2% (from +6.9%), while the pre-crisis levels of activity are expected to be reached in early 2023. We expect at least EUR20 billion in additional fiscal relief measures to be announced in 2021. As a consequence the French government is unlikely to curb the public debt increase next year. We expect the debt-to-GDP ratio to reach 120% of GDP in 2021 (up from 117.5% in 2020).
In Italy, the lack of a strong fiscal policy tailwind is likely to weigh on its growth performance at the turn of 2020/21. Preliminary Q3 GDP data for Italy shows a strong rebound of +16.1% q/q in Q3, driven by private consumption as well as strong external demand. This is reflected in robust industrial production, which, thanks to the economy’s position in the global value chain, is now close to pre-crisis levels. However, infections have increased since mid-October. While the dynamic remains weaker than in France or Spain, some restrictive measures have been restored, targeted at bars and restaurants (reduced opening hours), as well as leisure and cultural activities (entirely closed). But there are major differences among regions, with measures in the Northern economic strongholds being closer to the soft lockdown in Germany. That means that the Italian retail and industrial sector remains fully working. Nevertheless, a Q4 GDP contraction is all but certain. In addition to the effect of the confinement measures, industrial momentum is likely to weaken due to inventory reductions. We expect economic activity to drop by -3.0% q/q in Q4 and the recovery is likely to remain muted in early 2021 since we see the risk of a fiscal stimulus gap despite more announcements on the fiscal front (the Italian government has approved an additional package of compensatory measures worth EUR5.4bn combining grants, tax deferrals/cancellations and the extension of the short-term work scheme until January 2021). In particular, several support measures for households and businesses could come to an end at the turn of the year. Moreover the measures from the national recovery plan (EUR150bn according to the draft by the Ministry for Economic Development) are mainly supply-side-oriented and have longer lead times, which will hardly allow for a quick implementation. All this means that we have revised our GDP growth forecasts. Even with a setback of -3.0% q/q in Q4 we now expect real GDP to contract by –9.0% in 2020 (-10.1% previously). At the same time, with the adverse carry-over of Q4, we need to adjust our GDP growth forecast for 2021 to +3.8% (previously +4.1%).
Spain lags its European peers in sanitary and fiscal response. Q3 GDP growth was also stronger than expected, but activity was still -9.1% below pre-crisis levels. This time around, new lockdowns or confinamiento should also be “light” for the Spanish economy (closing of non-essential services but continuation of construction, manufacturing and education) and hence less damaging: we estimate the monthly shock could be 40% of that of April i.e. activity would run at close to 86% of October levels. Therefore, with a one-week lockdown in the country’s economic centers, GDP could contract by around -2% q/q in Q4. However, it is likely that the government will also announce a month-long national lockdown in the next days or weeks, given that new cases have kept hitting new record highs in the past week. This leads us to revise our previous GDP forecast for Q4 from -1.3% q/q to -5.5% q/q. December would see a recovery but in Q1 restrictions would remain tighter than after the first confinamiento, leading to a meagre +1% q/q growth then. Spain’s laggard status in the Eurozone should be confirmed: After a contraction of –12.1% in 2020 we expect a a recovery of only +4% in 2021 due to high unemployment, still very subdued tourism activity and uncertainty around the EUR72bn stimulus adoption and implementation. Real economic activity would remain -8% below pre-crisis levels at the end of 2021.
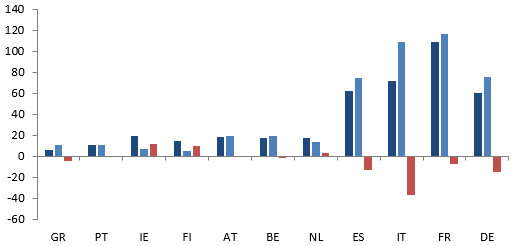
The government announced in late summer 2020 that it would unlock an additional EUR11bn to fund partial employment schemes (ERTE) until 31 January 2021, i.e. around EUR2.2bn per month (equivalent to subsidizing around 800,000 workers). However, we calculate that 50-60% of workers who received partial employment benefits during the first lockdown could need to receive them again in case of a second lockdown. Our estimates point to an additional EUR2.5bn spent over the lockdown month and in total between EUR3.5bn and EUR4bn of additional spending until 31 January (around 0.4% of GDP). Yet the Spanish government is also likely to extend public guarantees, which had been successful during the first wave. In total, we estimate that around 1.5-2% of GDP in additional spending would be needed to avoid a corporate solvency crisis during this second round of lockdowns. It is also worth remembering that during Q2, state subsidies to non-financial corporates tripled, which combined with lower costs linked to compensation of employees (-17% q/q) managed to protect corporate margins (+1.6pp to 39.9%) and keep cash from operating activities (net savings) stable compared to 2019.
In the UK, Brexit is likely to act as a drag on the post-lockdown recovery. The cost of the second lockdown is expected to go up to one third of the previous one. Social spending, primarily impacted by the lockdown measures, accounts for 48% of GDP. Hence, by accounting for two thirds of the previous lockdown impact from April, and a limited recovery in the rest of the economy, we forecast GDP growth to fall by around -9% m/m in November and to recover only slightly in December (+2% m/m) if a limited reopening is possible around Christmas. Overall, we expect Q4 GDP to fall between –5% and –6% q/q. Fiscal relief measures similar to the ones from March have been reactivated (partial unemployment scheme, tax and mortgage repayments deferrals, public guaranteed schemes), which should add around 1.5-2pp of GDP to public debt. However, the fiscal relief measures coupled with additional QE purchases to the tune of GBP100bn by year-end (the equivalent of 5% of GDP) will play a significant stabilizer role and keep solvency risks in check. Our baseline scenario (a last-minute deal with the EU) has considerably gained traction during the past two weeks, notably as the sanitary situation has worsened across Europe. On the back of the generalized (lighter) lockdowns in Europe, a (short) technical extension of the transition period is likely to avoid disruption at the border due to the custom checks implementation on the date of the EU exit. Hence, Brexit is expected to cut -2.5pp from the recovery post lockdown in Q2 (to 4.5% q/q). Overall, we expect GDP growth to reach +2-2.5% in 2021 as the cost of Brexit would not be fully compensated for by the expected fiscal stimulus (around 3% to 4% of GDP, mainly focused on infrastructure spending and lowering consumer taxes to reduce the burden of higher import prices post Brexit).