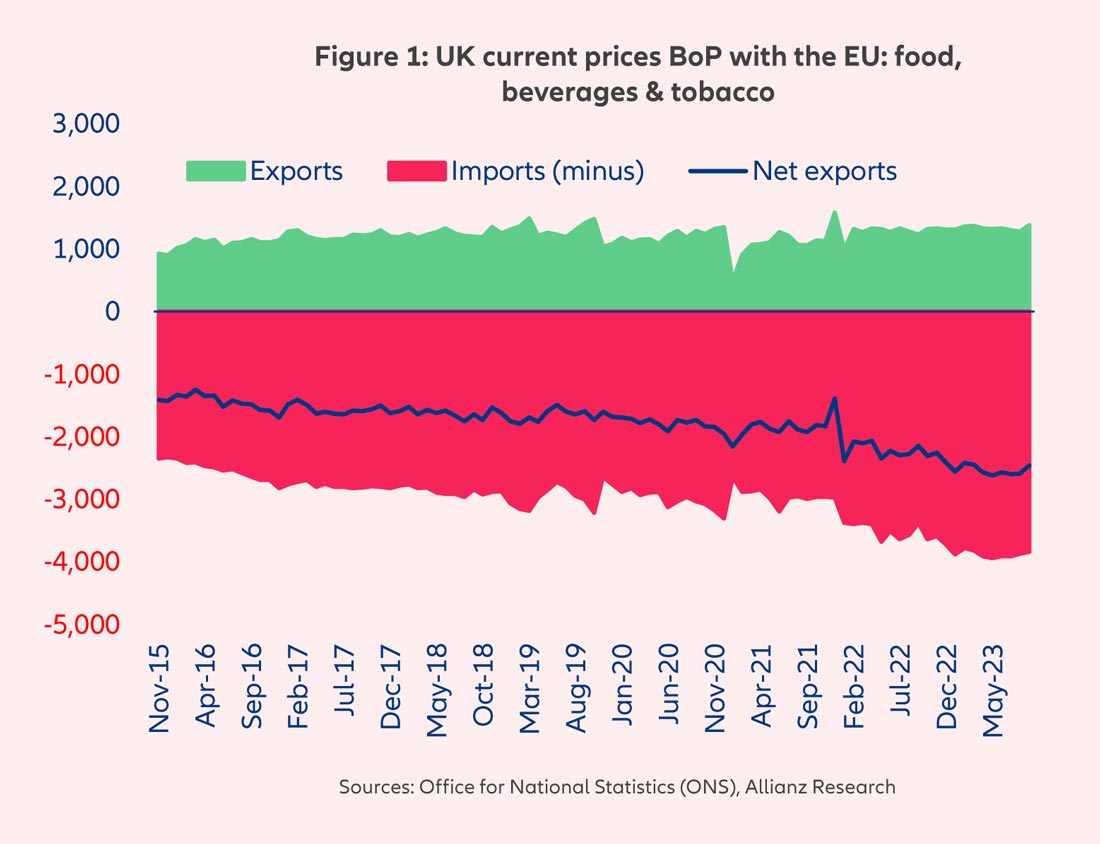
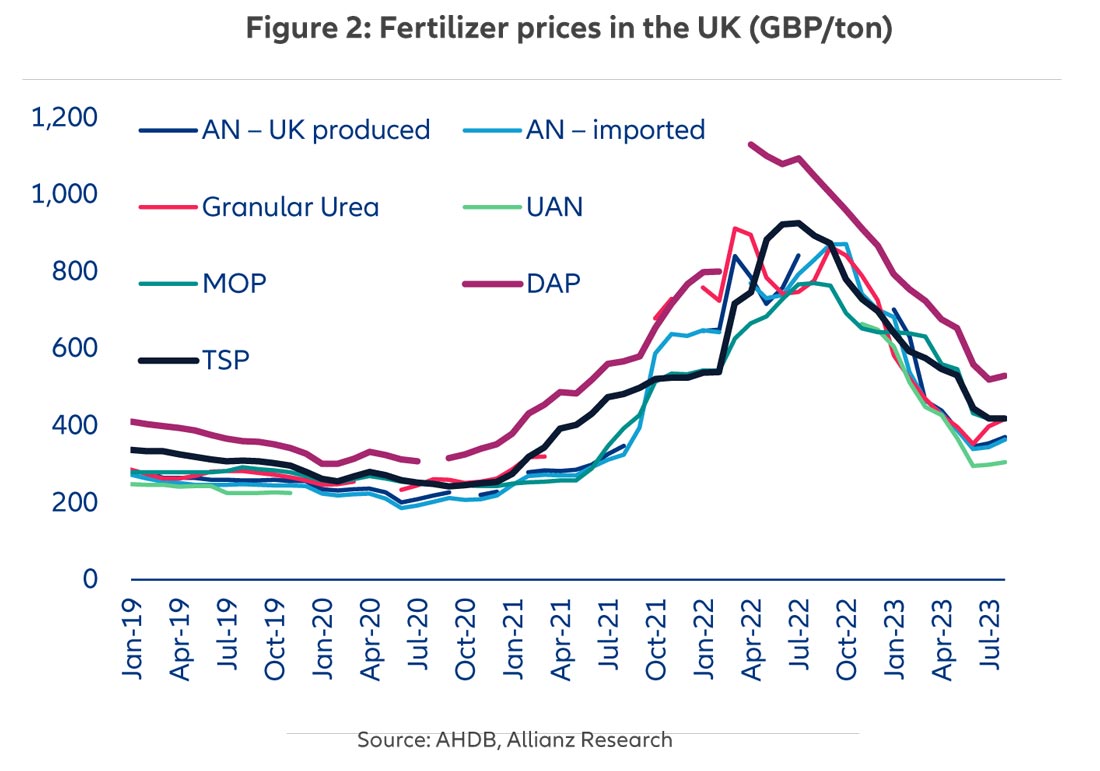
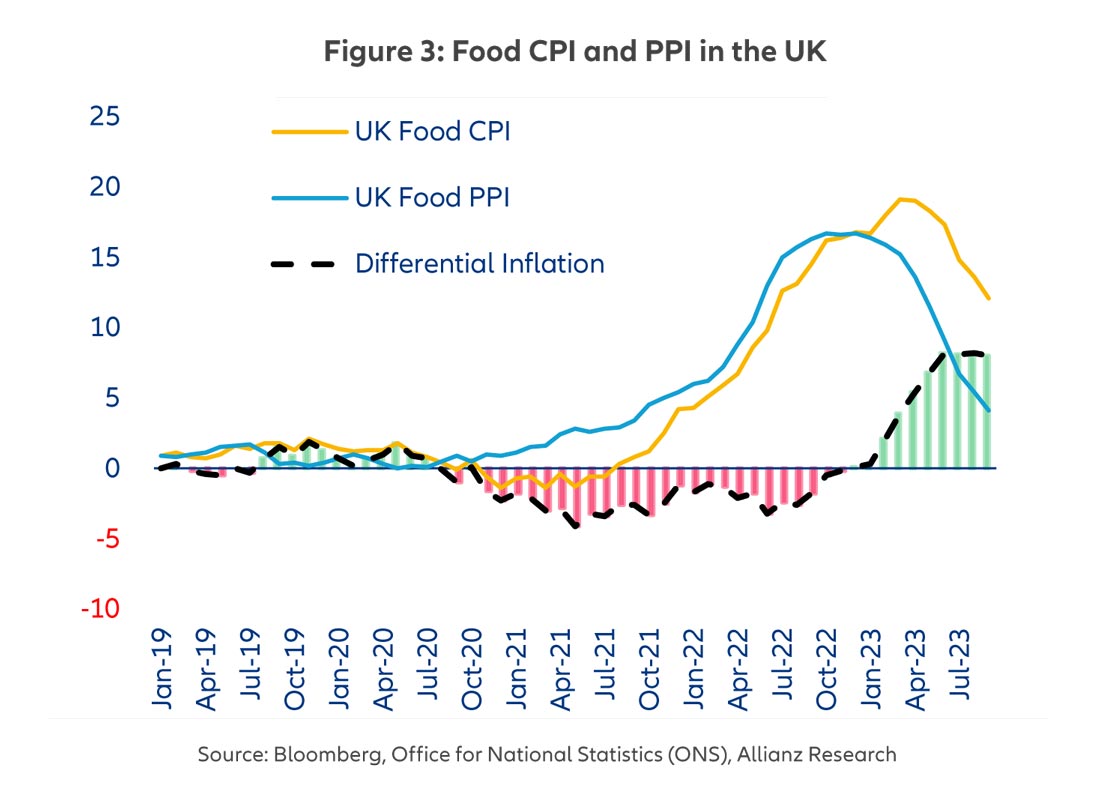
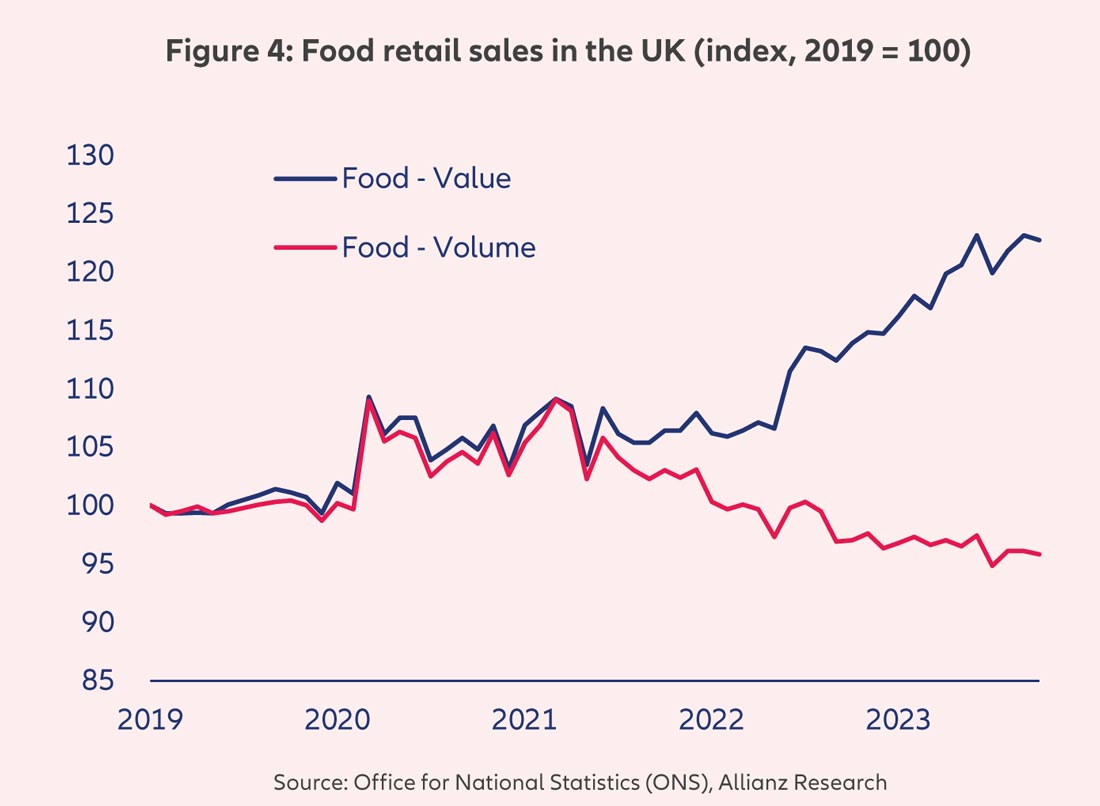
Russia is the world's largest supplier of natural gas and is responsible for 33% of the world’s fertilizer production. As a result, the trade sanctions imposed on Russia tightened the supply of fertilizers globally throughout 2022 and 2023, while in parallel, other key fertilizer-producing countries, such as Germany, were forced to limit production due to high energy costs. At one point in late 2022, around 70% of Europe’s ammonia production capacity was substantially reduced or shut down. The aftermath has been an unprecedented increase in the price of fertilizers, which represent around 12% of input costs of field crop farms. In the UK, for example, fertilizer prices more than tripled and peaked in summer 2022 (Figure 2). Fortunately, so far in 2023, they have become more affordable as a reflection of declining natural gas prices. However, lingering supply issues amid an inflationary backdrop mean prices will remain above historical averages for the next few quarters, alongside those of most soft commodities.